تعلم الهندسة معنا.. أينما كنت
شروحات هندسية عملية، أدلة مفصلة، ومصادر مجانية في مختلف التخصصات.
ابدأ التعلم الآنشروحات هندسية عملية، أدلة مفصلة، ومصادر مجانية في مختلف التخصصات.
ابدأ التعلم الآندليل المهندس للمسامير والصواميل: من اختيار النوع إلى الرسم الهندسي( مكتبة AutoCAD مجانية)
1. ما الفرق بين المسمار (Bolt) والبرغي (Screw):
قبل الغوص في الأنواع، يجب التمييز بينهما هندسيًا:
• المسمار (Bolt): صُمم ليُستخدم مع صامولة لتثبيت قطعتين غير مقلوظتين معًا.
• البرغي (Screw): يُربط مباشرة في ثقب يحتوي على قلاوظ داخلي (Tapped Hole).
2. أشهر أنواع المسامير واستخداماتها (Bolts Types)
يحدد شكل رأس المسمار الأداة المستخدمة في الربط والمساحة المطلوبة للتصميم:
• مسامير الرأس السداسي (Hex Head): الأكثر شيوعًا في الهياكل المعدنية لسهولة ربطها بعزم دوران عالٍ.
• مسامير الألن (Socket Head): الحل الأمثل في الماكينات الدقيقة والأماكن الضيقة حيث لا توجد مساحة لاستخدام مفتاح الربط الخارجي.
• المسامير الغاطسة (Countersunk): تُستخدم عندما تريد سطحًا أملسًا تمامًا، كما هو الحال في أجزاء الماكينات المتحركة أو التصميمات الجمالية.
3. أنواع الصواميل ووسائل الأمان (Nuts Types)
لا تكتمل الوصلة المسمارية بدون صامولة مناسبة، وتتعدد أنواعها حسب درجة الأمان:
1. الصامولة السداسية (Hex Nut): الخيار القياسي لكافة التطبيقات.
2. صامولة التأمين (Lock Nut): تحتوي على حلقة نايلون تمنع الفك التلقائي نتيحة الاهتزازات.
3. الصامولة المجنحة (Wing Nut): مثالية للتطبيقات التي تتطلب فكًا وتركيبًا يدويًا متكررًا دون أدوات.
4. كيف تختار رتبة المسمار (Bolt Grade):
السر الذي يميز المهندس المحترف هو قدرته على قراءة الأرقام المحفورة على رأس المسمار. هذه الأرقام تحدد مقاومة الشد (Tensile Strength).
| الرتبة (ISO) | المادة | الاستخدام |
| 4.8 / 5.6 | فولاذ منخفض الكربون | أحمال خفيفة وتطبيقات منزلية |
| 8.8 | (High Tensile) فولاذ متوسط الكربون | المعيار الذهبي في الماكينات والسيارات |
| 10.9 / 12.9 | فولاذ سبائكي معالج | أحمال ديناميكية عالية وتطبيقات حرجة |
💡 نصيحة Tech Fedny: عند استخدام SolidWorks Simulation، تأكد من اختيار مادة المسمار بناءً على الـ Grade لتكون نتائج معامل الأمان (Factor of Safety) دقيقة ومطابقة للواقع
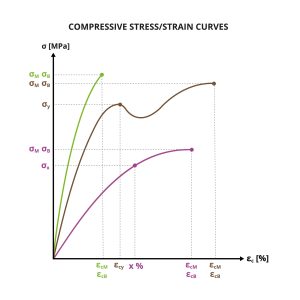
Series of compressive stress/strain curves for different materials
💡 نصيحة احترافية للمصممين: عند العمل على برنامج SolidWorks Simulation لإجراء تحليل إجهادات (Static Analysis) لوصلة مسمارية، تأكد من إدخال قيمة (Yield – Strength) الصحيحة بناءً على الـ Grade المختار، لضمان دقة معامل الأمان (Factor of Safety) في تصميمك.
5. المقاسات والأكواد القياسية (Standards)
تُصنّع المسامير عالميًا وفق معايير تضمن التوافق:
• النظام المتري (Metric): يرمز له بحرف M (مثل M10)، حيث يعبر الرقم عن القطر الخارجي بالمليمتر.
• المواصفات: أشهرها DIN (ألماني) و ISO (عالمي)، وهما المعتمدان في معظم ملفات الـ CAD.
6. استخدامات المسامير في المشاريع الهندسية
تتنوع التطبيقات لتشمل:
• تجميع الهياكل المعدنية (Steel Structures).
• خطوط الإنتاج والماكينات الصناعية.
• تصميم المظلات المعدنية (Canopies) والجمالونات.
7. تحميل مكتبة AutoCAD للمسامير والصواميل 📎
لتوفير وقتك في الرسم من الصفر، أعددنا لك ملف AutoCAD يحتوي على رسومات 2D دقيقة للمقاسات القياسية.
مميزات الملف:
• مطابق لمواصفات DIN و ISO.
• مقاسات جاهزة من M3 إلى M30.
• مثالي للوحات التنفيذية (Shop Drawings).
💾 (حمّل ملف AutoCAD للمسامير والصواميل من هنا)
الخلاصة
اختيار المسمار الصحيح ليس مجرد تفصيل صغير، بل هو قرار هندسي يتعلق بالأمان والكفاءة. فهمك للأنواع والرتب والمقاسات سيجعل تصميماتك أكثر قوة واحترافية.
Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Drawings
1. What Are Mechanical Engineering Drawings? (Technical Definition)
Mechanical engineering drawings are standardized technical documents used to describe mechanical parts and systems with accuracy. They communicate geometry, dimensions, tolerances, materials, and surface finish clearly.
Unlike freehand sketches, these drawings follow strict engineering standards. As a result, manufacturers can produce components without additional explanation. In practice, each drawing acts as a technical contract between the designer and the manufacturer.
2.Main Elements of Mechanical Drawings
Every professional mechanical drawing includes several key elements.
These views represent the complete geometry of the component:
Orthographic views (front, top, side)
Section views for internal features
Isometric views for visualization
Together, these views ensure the part is fully understood.
Dimensions and tolerances are essential elements in mechanical engineering drawings. They define how a part should be manufactured and how accurately it must fit with other components.
Dimensions describe the exact size of a mechanical component. They include linear dimensions such as length, width, and diameter, as well as angular dimensions.
Clear and accurate dimensions ensure that each part is manufactured to the correct size. Without proper dimensioning, production errors become unavoidable.
Tolerances specify the allowable variation from a nominal dimension. In practice, perfect accuracy is impossible during manufacturing.
Therefore, tolerances allow controlled deviations while still ensuring proper assembly. As a result, parts can fit together without excessive tightness or looseness.
Geometric tolerances control shape, orientation, and position. In addition, they define requirements such as flatness, parallelism, and concentricity.
Consequently, GD&T improves functional performance and reduces unnecessary manufacturing costs.
Poor tolerance selection can lead to assembly failure or excessive wear. However, correct tolerancing improves reliability and product lifespan.
For this reason, tolerances are one of the most critical aspects of mechanical engineering drawings.
3. Types of Mechanical Engineering Drawings:
| Showing how parts fit together | Assembly Drawing |
| Assembly sequence clarification | Exploded View |
| Functional relationship, not scale | Schematic Drawing |
| On-site assembly guidance | Installation Drawing |
Each type serves a specific stage of the engineering workflow.
4.Engineering Standards Used in Drawings
Mechanical drawings must follow international standards to ensure global understanding. Common standards control line types, symbols, and dimensioning rules.
As a result, engineers from different countries can read the same drawing without confusion. Standards also give drawings legal and technical validity.
5. Reading vs Designing Drawings (Important Distinction)
Not every engineer designs drawings, but every mechanical engineer must read them correctly.
• Design engineers create drawings
• Manufacturing engineers interpret them
• Maintenance engineers rely on them for repairs
• Quality engineers inspect parts based on drawings
Misreading a drawing can lead to catastrophic mechanical failure.
6. Manual Drafting vs CAD Drawings
In the past, drawings were created manually using drafting tools. However, modern engineering relies on CAD software.
CAD drawings offer higher accuracy, faster revisions, and easy integration with manufacturing systems. Therefore, CAD has become the industry standard.
7. Role of Mechanical Drawings in Industry
Mechanical drawings play a vital role in many industries. For instance, they are used in machine design, CNC manufacturing, automotive systems, and power plants.
In addition, maintenance teams rely on drawings for repairs and spare parts identification. Simply put, industrial production cannot function without accurate drawings.
Engineering+Working+Drawing+Basics
8. Conclusion
Mechanical engineering drawings are more than simple sketches. They are a technical language governed by strict rules and standards.
Therefore, understanding mechanical drawings is a fundamental skill for every mechanical engineer. It is the first step toward professional engineering practice.

فِدني تك هي منصة تعليمية هندسية تهدف إلى تقديم محتوى احترافي مبسّط يساعد الطلاب والمهندسين على فهم الأساسيات وبناء مهارات قوية في مجالات الهندسة المدنية، المعمارية، الميكانيكية، الكهربائية، الري، واللاندسكيب.
نؤمن في فِدني تك أن المعرفة يجب أن تكون واضحة، عملية، وقابلة للتطبيق. لذلك نقدم شروحات هندسية دقيقة، أمثلة واقعية من سوق العمل، وحلولًا مبسّطة للمشكلات التي قد تواجه أي مهندس أو طالب في بداية طريقه.
اكتشف المزيدتخطيط وإدارة موارد المياه وأنظمة الري الحديثة
الأنظمة الميكانيكية، خطوط الإنتاج والتحليل الهندسي
أنظمة الجهد المنخفض والعالي، تصميم اللوحات والتحكم
الدوائر الإلكترونية، تصميم الأنظمة المدمجة والاتصالات
الطاقة الشمسية، طاقة الرياح وحلول الطاقة المستدامة
ديناميكا الهواء، تصميم هياكل الطائرات وأنظمة الدفع
تصميم المنشآت الخرسانية والمعدنية، إدارة مشاريع البناء
تصميم المباني، التخطيط الحضري، ورسم المشاريع المعمارية
تطوير مهارات اللغة الإنجليزية الخاصة بالهندسة والتواصل المهني
لا توجد كتب منشورة لعرضها حاليًا. الرجاء إضافة كتاب واحد على الأقل في قسم Library Books.